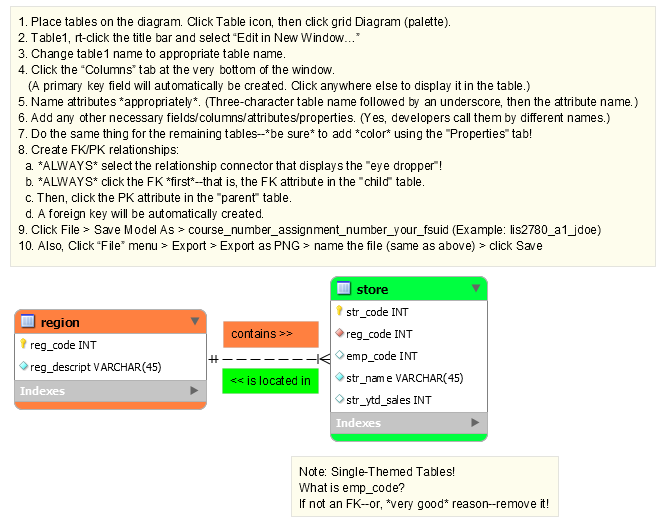
Database Resources
Mark K. Jowett, Ph.D.
A collection of links and resources that you may find helpful!
Three Rules of DB Design and CASE Tool (Data Modeling)
- Unless otherwise stated, *ALL* ERDs require http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/workbench/, submitted in .mwb file format.
- Entity Integrity: *All* tables must have a PK, and the PK cannot be null (by definition, *must* be unique).
- Referential Integrity: FKs *must* match the values of their PKs in their parent tables, including data types (or, may be null, depending upon the business rules)!
- Normalization: Single-themed tables! (3NF):
Mnemonic: All nonkey attributes must depend upon the key (1NF), the whole key (2NF), and nothing but the key (3NF)!
Steps: Normalization_Steps.pdf
Auto Increment VS GUID/UUID
IMPORTANT! - Auto Increment VS GUID/UUID:- What is a UUID?
- What is a GUID?
- The Quick Guide to GUIDs
- UUID vs GUID
"The term GUID usually refers to Microsoft's implementation of the Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) standard." An updated quote from the same Wikipedia article: RFC 4122 itself states that UUIDs "...are also known as GUIDs". All this suggests that "GUID", while originally referring to a variant of UUID used by Microsoft, has become simply an alternative name for UUID… Sources: Universally unique identifier Is there any difference between a GUID and a UUID?Which Should Be Used?!
NEW! MySQL 5.7 (specifically, MySQL 5.7.5 and later) GROUP BY clause In short: SQL92 and earlier does *not* permit queries for which the SELECT list, HAVING condition, or ORDER BY list refer to nonaggregated columns that are not named in the GROUP BY clause. SQL99 and later permits such nonaggregates *if* they are functionally dependent on the GROUP BY columns: That is, *if* the primary key (or key attribute) of a nonkey attribute (used in the SELECT clause) is used in the GROUP BY clause. Solutions: 1) Include *all* non-key, nonaggregate attributes from SELECT clause in GROUP BY clause. Or... 2) Make non-key, nonaggregate attributes from SELECT clause functionally dependent upon GROUP BY columns, by using their primary keys in the GROUP BY clause! More information (and example) can be found here: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/group-by-handling.html And, here: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34115174/error-related-to-only-full-group-by-when-executing-a-query-in-mysql BTW, disabling the default setting is *NOT* recommended.
Databases vs Spreadsheets
Database Rankings, SQL History, NoSQL
DB-Engines RankingSQL History
NoSQL systems may be catching up?
MongoDB (NoSQL database)
- Getting started: http://docs.mongodb.org/getting-started/shell/
- Tutorial: http://www.tutorialspoint.com/mongodb/
- Installation: http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/installation/
- MongoDB Hosting: https://mongolab.com/
- Quick-Start Guide to MongoLab: http://docs.mongolab.com/
- The Little MongoDB Book: http://openmymind.net/mongodb.pdf
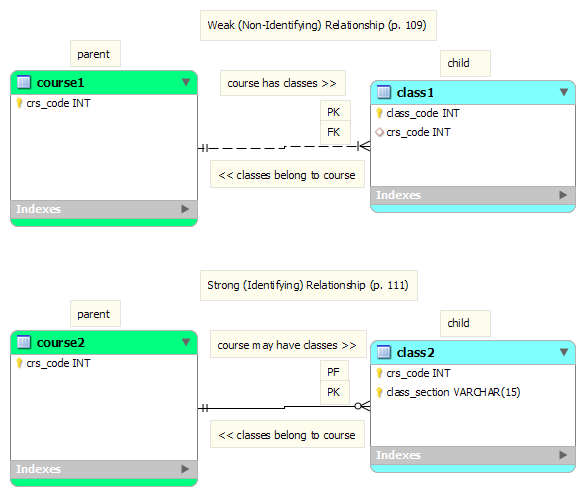
Relationships: Weak and Strong
Forward/Backward-Engineering Databases (ERDs)
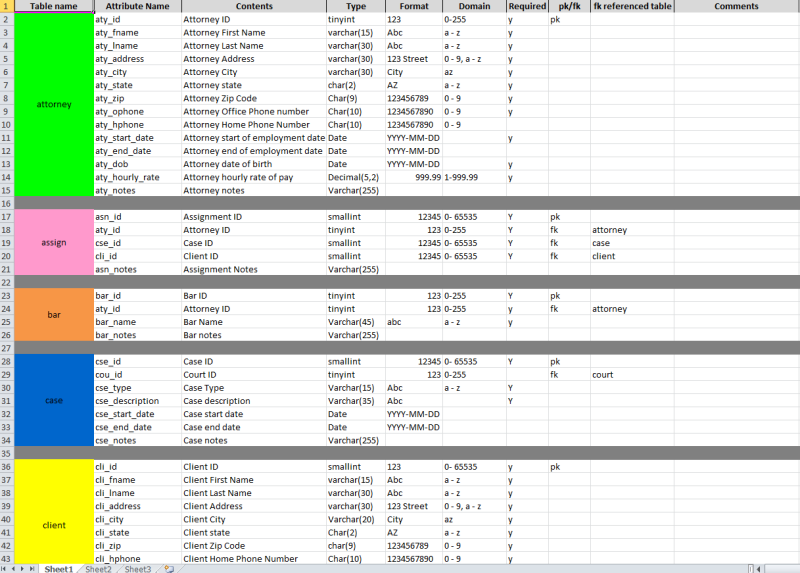
Data Dictionary Example
SQL Statements
(Uses Premiere database: details bottom of page)SQL - Quick Reference
Log in to *YOUR* database using MySQL Workbench, AND through SSH:
Notes > MySQL Workbench and SSH Login Procedures:
1. Using MySQLWorkbench, AND
2. Using SSH Client (a. Windows, b. Mac)
Overall database reports:
Display user, timestamp, and MySQL version:
select user(), now(), version();Display your grants:
show grants;Display the databases for which you have access:
show databases;Upload table structures and data:
***First: BACKUP *ALL* existing tables! See (Simple) Backup below. Then...
drop database if exists yourusername; create database if not exists yourusername; use username; source db/premiere.sql --or... \. db/premiere.sqlDatabase Schema and Metadata:
Display all tables in database:
show tables;Display structure (metadata) for each table:
describe customer; describe order_line; describe orders; describe part; describe sales_rep;Display customer table create statement (and additional table information):
show create table customer; show full columns from customer;Display database metada:
1. Upload file to db directory on CCI server: mymetadata.sql 2. Log into MySQL 3. Type following command: \. db/mymetadata.sql"CRUD": Create, Read, Update, Delete
- SELECT: read (retrieve) data
- INSERT: create (add) data
- UPDATE: modify data
- DELETE: remove data
Order of SELECT SQL clauses:
- SELECT: list of columns to be included in result set. An asterisk (*) can be used to specify all columns of the queried tables.
- FROM: table(s) from which data is to be retrieved (can include optional JOIN subclauses for joining tables).
- WHERE: conditional list restricts rows returned by query. Eliminates all rows from result set which do not evaluate to true.
- GROUP BY: used in conjunction with SQL aggregation functions (e.g., count, sum, min, max, avg, etc.), or to eliminate duplicate rows from result set. Used to project rows having common values into smaller set of rows.
- HAVING: filter rows resulting from the GROUP BY clause. Aggregation functions can be used in HAVING clause.
- ORDER BY: columns used to sort query result set (asc or desc, default: asc).
Examples:
SELECT Statement Syntax:SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table1, table2, ... [WHERE Clause] [GROUP BY clause] [HAVING clause] [ORDER BY clause];
- column includes one or more columns from tables, which data is retrieved.
- table is name of table(s), separated by commas, from which information is retrieved
- Code within brackets is optional.
- WHERE clause is used to retrieve specific information from a table excluding irrelevant data.
- GROUP BY clause is used with aggregate (group) functions (e.g., sum, min, max, count, etc.) to retrieve summarized data according to one or more columns (attributes).
- Having clause is used to filter data based on group functions. Similar to WHERE condition, but used with group functions. Group functions CANNOT be used in WHERE clause, but can be used in HAVING clause.
- ORDER BY clause is used to sort results either in ascending or descending order (asc or desc, default: asc).
NOTE: GROUP BY clause should contain all columns in SELECT list, except those used in group functions.
NOTE: When WHERE, GROUP BY, and HAVING clauses are used together in SELECT statement, the WHERE clause is processed first, then the rows that are returned after the WHERE clause is executed are grouped based on the GROUP BY clause. Finally, any conditions on the group functions in the HAVING clause are applied to the grouped rows before the final output is displayed.
SELECT Statement Usage:
List all customers:
select * from customer; +-----------------+----------+-------+------------+---------+-------+----------+---------+--------------+---------------+ | customer_number | last | first | street | city | state | zip_code | balance | credit_limit | slsrep_number | +-----------------+----------+-------+------------+---------+-------+----------+---------+--------------+---------------+ | 124 | Adams | Sally | 481 Oak | Lansing | MI | 49224 | 818.75 | 1000.00 | 03 | | 256 | Samuels | Ann | 215 Pete | Grant | MI | 49219 | 21.50 | 1500.00 | 06 | | 311 | Charles | Don | 48 College | Ira | MI | 49034 | 825.75 | 1000.00 | 12 | | 315 | Daniels | Tom | 914 Cherry | Kent | MI | 48391 | 770.75 | 750.00 | 06 | | 405 | Williams | Al | 519 Watson | Grant | MI | 49219 | 402.75 | 1500.00 | 12 | | 412 | Adams | Sally | 16 Elm | Lansing | MI | 49224 | 1817.50 | 2000.00 | 03 | | 522 | Nelson | Mary | 108 Pine | Ada | MI | 49441 | 98.75 | 1500.00 | 12 | | 567 | Dinh | Tran | 808 Ridge | Harper | MI | 48421 | 402.40 | 750.00 | 06 | | 587 | Galvez | Mara | 512 Pine | Ada | MI | 49441 | 114.60 | 1000.00 | 06 | | 622 | Martin | Dan | 419 Chip | Grant | MI | 49219 | 1045.75 | 1000.00 | 03 | +-----------------+----------+-------+------------+---------+-------+----------+---------+--------------+---------------+List credit limit for customer number 256:
select credit_limit from customer where customer_number=256; +--------------+ | credit_limit | +--------------+ | 1500.00 | +--------------+List the zip codes that have the highest customer balance more than $1000 (use alias max_balance):
SELECT zip_code, MAX(balance) as max_balance FROM customer GROUP BY zip_code HAVING MAX(balance) > 1000 ORDER BY balance desc; +----------+-------------+ | zip_code | max_balance | +----------+-------------+ | 49224 | 1817.50 | | 49219 | 1045.75 | +----------+-------------+NOTE: Aliases are used to help organize or simplify output. Both column (attribute) and table aliases may be used.
INSERT Statement Syntax (using attribute names):
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME [(col1, col2, col3,...colN)] VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...valueN);NOTE: col1, col2,...colN -- names of columns (attributes) in table into which data is to be inserted.
INSERT Statement Usage (using attribute names):
Add a customer record:
INSERT INTO customer
(customer_number, last, first, street, city, state, zip_code, balance, credit_limit, slsrep_number)
VALUES
('999','Doe','Jane','456 Elm Ave.','Panama City','FL','32445',700.00,900.00,'12');
INSERT Statement Usage (using attribute names), multiple rows:Add three customer records:
INSERT INTO customer
(customer_number, last, first, street, city, state, zip_code, balance, credit_limit, slsrep_number)
VALUES
('999','Doe','Jane','456 Elm Ave.','Panama City','FL','32445',700.00,900.00,'12'),
('777','Doe','John','123 Main St.','Tallahassee','FL','32304',500.00,600.00,'06'),
('888','Doe','Baby','789 Forest Ct.','Tallahassee','FL','32305',800.00,9500.00,'03');
NOTE: When inserting data to *all*
columns (attributes), column names can be omitted from sql
query. However, make sure order of values is in same order as columns
in table.
INSERT Statement Syntax (NOT using attribute names):
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...valueN);INSERT Statement Usage (NOT using attribute names):
Add a customer record:
INSERT INTO customer
VALUES
('777','Doe','John','123 Main St.','Tallahassee','FL','32304',500.00,600.00,'06');
INSERT Statement Usage (NOT using attribute names), multiple rows:Add three customer records:
INSERT INTO customer
VALUES
('999','Doe','Jane','456 Elm Ave.','Panama City','FL','32445',700.00,900.00,'12'),
('777','Doe','John','123 Main St.','Tallahassee','FL','32304',500.00,600.00,'06'),
('888','Doe','Baby','789 Forest Ct.','Tallahassee','FL','32305',800.00,9500.00,'03');
NOTE: When adding records, only character or date
values need to be enclosed with single quotation marks
(use describe statement).
UPDATE Statement Syntax:
UPDATE table SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ... [WHERE condition];
- table to be updated
- column that gets modified
- value that is assigned to column (attribute)
- Code within brackets is optional.
- WHERE clause identifies rows that are affected
UPDATE Statement Usage:
Modify a customer record:
UPDATE customer SET balance=0.00, credit_limit=3000.00 WHERE customer_number=256;Modify *ALL* customer records:
UPDATE customer SET balance=0.00, credit_limit=3000.00;Careful NOTE!: Without WHERE clause, *ALL* column rows are affected!
DELETE Statement Syntax:
DELETE FROM table [WHERE condition];
- table data to be deleted
- Code within brackets is optional.
- WHERE clause identifies rows that are affected
DELETE Statement Usage:
Delete a customer record:
DELETE FROM customer WHERE customer_number = 256;Delete *ALL* customer records:
DELETE FROM customer;
ALTER Statement:
MySQL Server Version
To add a column at a specific position within a table row, use FIRST or AFTER col_name.
The default is to add the column last. You can also use FIRST and AFTER in CHANGE or MODIFY operations to reorder columns within a table.
Example:
Add a "comments" attribute before the "url" attribute in the dealership table (varchar 255), it cannot be null, and set the default value to "testing."
describe dealership; ALTER TABLE dealership add dlr_comments varchar(255) not NULL default 'testing' AFTER dlr_ytd_sales; describe dealership;
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/alter-table.html
MS SQL Server Version
-- NOTE: Currently, there is no direct way to alter order for columns in SQL Server. -- Get table info, including foreign keys (similar to "describe" in MySQL), before/after EXEC sp_help 'dbo.mytable'; ALTER TABLE dbo.mytable insert tbl_attribute varchar(255) NULL default 'testing'; EXEC sp_help 'dbo.mytable';
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190238.aspx
Formatting Data
MySQL Server version:
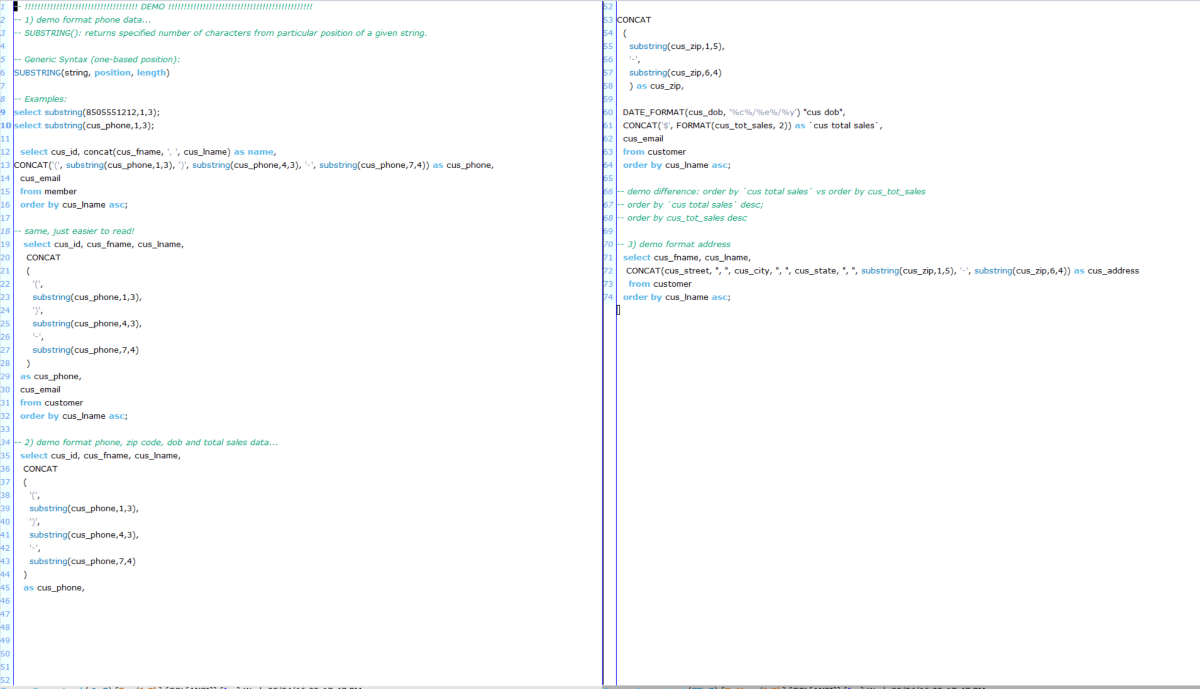
MS SQL Server version:
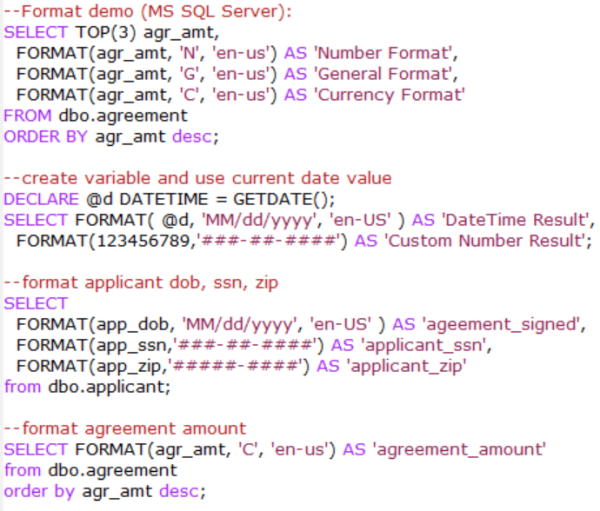
Transactions
MS SQL Server version:
-- Remember: cannot use "start" transaction in MS SQL Server
-- show data before/after
begin transaction;
select * from mytable;
//do something...
select * from mytable;
commit;
Views
MS SQL Server version:
-- MS SQL SERVER example:
create view dbo.v_myview as
select cus_fname, cus_lname...
from dbo.customer
order by cus_lname desc;
go
Stored Procedures
MS SQL Server version:
-- With MS SQL Server, no need to change delimiter (go command interpreted as end of CREATE PROCEDURE statement) CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.MyStoredProc AS -- check data before select * from dbo.mytable; //do something -- check data after select * from dbo.mytable; GO EXEC dbo.MyStoredProc; GO
Database Administration (DBA)
- Granting_Privileges.pdf
- create_region_store.sql
- MySQL_Administrator_Tutorial.pdf
- MySQL_Installation_Admin_Brief.pdf
- MySQL_Installation_Admin_Brief.pdf
- lis3781_permissions.pdf
- Enforcing_PK_FK_Relationship.pdf
- create_region_store.sql
Integrate these two sections (remove duplicates)!
Securing Data
There is much research and information online concerning hashing/encrypting data:
- http://www.danielmiessler.com/study/encoding_encryption_hashing/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4948322/fundamental-difference-between-hashing-and-encryption-algorithms
-- convert string "test" into SHA2 512 hash value
select sha2('test',512);
-- length as hex value:
select length(sha2('test',512));
-- length as binary
select length(unhex(sha2('test',512)));
hash_functions.sql
Example:
Use MySQL's intrinsic sha2() hash function on randomized SSNs.
Generate binary sha2 value (converted from hexadecimal format), and store as binary(64) data type (fewer storage bytes).
***Note***: the following example should *NOT* be used in a production environment. This is only for demo purposes!
-- generate random 9-digit number, convert SHA2 Hash value into binary SELECT unhex(sha2(FLOOR(000000000 + (RAND() * 1000000000)), 512)); -- example updating a randomized SSN using SHA2 hashing converted into binary update person set per_ssn=(SELECT unhex(sha2(FLOOR(000000000 + (RAND() * 1000000000)), 512))) where per_id=x;
Securing Data References:
Loading External Data
- Create .csv file with data, or use generatedata.com to create 100 records for table.
- *Be sure* to save file as .csv. Example: person.csv
- Save each generated .csv data file using the table name (as above).
- SFTP each .csv file to the "db" directory on the database server (i.e., /home/userid/db/). (Create db directory, if necessary.)
- Modify load_data_infile.sql to match your database design, as well as *your* userid.
- After modifying, SFTP load_data_infile.sql to *your* "root" directory (i.e., /home/userid/).
- Log into MySQL (using --local-infile option) and execute the load data infile command for each table. Example:
mysql -u fsuid -p --local-infile=1
- use your database
- turn off foreign key checking (to prevent pk/fk relationship errors)
- load source file (generic syntax):
- Example:
- *Be sure* to turn foreign key checking back on!
use databasename;
set foreign_key_checks=0;
source path_to_filename.sqlOr...
\. path_to_filename.sql
\. load_data_infile.sql
set foreign_key_checks=1;
(Simple) Backup
backup and load (note: "--databases" includes "use" database command):1) one database:
c:\mysql\bin>mysqldump -u username -p --port=3306 --databases database_name > database_name_yyyy_mm_dd.sqlMore than one database:
c:\mysql\bin>mysqldump -u username -p --port=3306 --databases db1 db2 > mydbs_date.sqlAll databases:
c:\mysql\bin>mysqldump -u username -p --port=3306 --all-databases > all_databases_date.sql2) load:
c:\mysql\bin>mysql -u username -p --port=3306 database_name < database_name_yyyy_mm_dd.sql(Stores file in the MySQL bin directory.)
Can change path:
../data/all_databases_date.sqlBackup, with Alternative Load Method (i.e., already logged into server):
- backup your database:
- Login (see above)
show databases;
use database;
show tables;
- view data:
select * from tablename;
- drop one or all tables:
drop table tablename1; drop tablename2;
- load your backed up database:
\. database_name_date.sql
Or, if path changed...
relative path:\. ../data/all_databases_date.sql
absolute path:\. C:\mysql\data\all_databases_date.sql
- list tables:
- view data:
c:\mysql\bin>mysqldump -u username -p --port=3306 databasename > databasename_date.sql
show tables;
select * from tablename;
backup and load all databases (with additional options):
1) backup:
c:\mysql\bin>
mysqldump -u username -p --port=3306 --all-databases --add-drop-database --single-transaction --events > path/all_databases_date.sql
2) load:
c:\mysql\bin>
mysql -u username -p --port=3306 < all_databases_date.sql
Additional backup/restore info:
http://www.devshed.com/c/a/MySQL/Backing-up-and-restoring-your-MySQL-Database/
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/backup-methods.html
MySQL and SQL Tips
- MySQL Tips
- DB Performance-Tuning
- MySQL Programs
- Invoking MySQL Programs
- mysqladmin (when using mysqladmin: must use user name and password)
- MySQL Connecting/Disconnecting
- Entering Queries
DATE_FORMAT() function used to display date/time data in different formats: %Y: represents year in four digits %m: represents month, numeric (00..12) %d: reprsents day of the month, numeric (00..31) To avoid miscalculations due to leap years:http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/date-and-time-functions.html#function_date-format
(For older versions of MySQL, prior to 5.5): 1. Subtract current year from birth year to get age. 2. If current month and date is less than birth month and date, subtract 1 from step 1 SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%Y') - DATE_FORMAT(dob, '%Y') - (DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '00-%m-%d') < DATE_FORMAT(dob, '00-%m-%d')) AS age
http://ma.tt/2003/12/calculate-age-in-mysql/
***Use this!***: As of MySQL 5.5+, timestampdiff can use curdate() or now() functions:
Generic syntax:
SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(time_unit_returned,start_date,end_date);Example:
SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(year, per_dob, now()) as age; -- returns age in yearshttp://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/date-and-time-functions.html#function_timestampdiff
Oracle
Resources:
Oracle Dual table DUAL is a table automatically created by Oracle Database along with the data dictionary. DUAL is in the schema of the user SYS but is accessible by the name DUAL to all users. It has one column, DUMMY , defined to be VARCHAR2, and contains one row with a value X. It is a special table used for evaluating expressions and/or calling functions. Oracle Dual table information: Oracle Dual Table Selecting from the DUAL Table
Resources
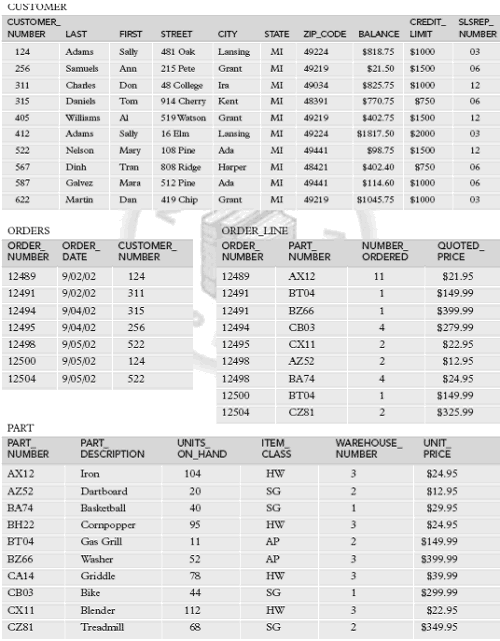
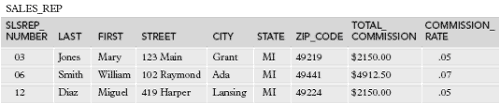
Data Resources:
Individual Premiere Table Files
Create:
Insert:
Database History
Edgar Codd obituary--Father of the "relational model" in 1970.Dr. Peter Chen--Introduced the entity relationship (ER) model in 1976.